Packets are routed to their destination as determined by a routing algorithm. The routing algorithm can create paths based on various metrics and desirable qualities of the routing path. For example, low latency may be of paramount concern and everything else is secondary, or a minimum hop count.
It's also entirely possible to have to weigh the various metrics against each other. For example, reducing the hop count could increase the latency to an unacceptable limit and some kind of balance would need to be found. For multi-parameter optimization, some form of optimization may be needed.
Once a route is determined for a packet, it is entirely possible that the route may change for the next packet, thus leading to a case where packets from the same source headed to the same destination could be routed differently.
Packet switching influenced the development of the Actor model of concurrent computation in which messages sent to the same address may be delivered in an order different from the order in which they were sent.

Your Friend

- Manpreet Singh Bindra
- PATIALA, PUNJAB, India
- Please Give Your Valuable Feedback manpreetsinghbindra@hotmail.com
Search Of Your Interest
4G Technology
(1)
AIRTEL Success Story
(1)
AREA NETWORKS
(1)
Apple 3G iPhones Improving Networking
(1)
BSNL DATAONE broadband disconnect problem
(1)
Basic Concept Of TELECOMMUNICATIONS SYSTEM
(1)
Basic and Simple Definition to 3G
(1)
Business Network
(1)
Business Strategy for Growth
(1)
Business Wireless Planning Strategy
(1)
CCTV IP camera
(1)
CISCO : how IGRP make large INTERNETWORKS in organizations
(1)
CISCO Solutions Provide
(1)
CTT6800+ -JPEG 2000 Compressed Transport Transceiver
(1)
Change of IP Address
(1)
Connectionless packet switching and routing
(1)
Core Network of 3G
(1)
Core Networking In MICROSOFT WINDOWS SERVER 2003
(1)
Current Protocols Essential Laboratory Techniques (CPET)
(1)
Difference between 2G - 3G - 4G & What is 4G & its Advantages ?
(1)
Different Business Networking Types
(1)
DirectX proportional to Networking
(1)
FREE Wi-Fi
(1)
Finisar :Traffic Generation
(1)
Fox Business Network
(1)
GPRS Core Network
(1)
HBR Technologies (HBR)
(1)
HOW TELEPHONE NETWORK SYSTEM WORKS
(1)
History of packet switching
(1)
How To Setup Wireless Connection(APPLY SAFETY SETTINGS FIRST)
(1)
How to Network 2 Computers Without a Hub or Router
(1)
How to Use a Wireless Network Connection with a Windows XP Portable Computer at Home and Work
(1)
How to make a proper website on NETWORKING
(1)
How to troubleshoot wireless network connections in Windows XP Service Pack 2
(1)
IP Addresses
(1)
Importance of BANDWIDTH in DSL Internet Connections
(1)
Internet and its Component
(1)
Introduction to LAN
(1)
Is Your Networking Caught A Virus?
(1)
Long Term Evolution (LTE)
(1)
MICROSOFT the WORLD WIDE LEADER in NETWORKING
(1)
Multi-Core Processing
(1)
Multi-core networking
(1)
NETWORKING CORE
(1)
NETWORKING IN MEDICAL APPLIANCES
(1)
NORTELVisitor-Based Networking Solution
(1)
Network Design
(1)
Network Protocols
(1)
Nokia Dual Sim Phones
(1)
OPTICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF LEDS
(1)
Packet switching in networks
(1)
Pressure Swing Adsorption(PSA)
(1)
Proxy Servers HIDE IP address from WEB NOT other INFORMATION
(1)
Purpose of Business Network or Networking
(1)
Role of EGP and BGP in the TCP/IP (Exterior Routing Protocols)
(1)
SOLUTION Providers to NETWORK Companies
(1)
STP topology of a Switched Network
(1)
STRUCTURED CABLES IN TELECOMMUNICATION
(1)
SeaTalk NG network
(1)
Setting Priorities for Next-Generation Web Apps - MICROSOFT
(1)
Social Network Services
(1)
Social Networking Services to Expand Business
(1)
Speed UP Your PC in 3 Easy Steps
(1)
Spyware affecting Networking
(1)
Sysinternals File and Disk Utilities
(1)
Sysinternals Networking Utilities
(1)
Sysinternals Security Utilities
(1)
TENA and NetAcquire
(1)
UNIX Network Security Architecture
(1)
WAN and Home Networking
(1)
What Network Administrators Think of NETWORKS
(1)
What Nortel Solutions can Provide? Case Study
(1)
Why Not Reserved IPs on Internet
(1)
WiMAX
(1)
Wireless Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
(1)
koollage-blogs-news
(1)
~ (DDBMS) DISTRIBUTED DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
(1)
~ ActiveVideo system
(1)
~ Advanced Shellcoding Techniques
(1)
~ Cisco VTP: VLAN Trunking Protocol
(1)
~ Features of the Web
(1)
~ How Core Networking Solve Problems?( Solutions provided by Core Networking)
(1)
~ Modulation Techniques for Wireless
(1)
~ Trillium Multi-Core Software
(1)
~ Wi-Fi Networking News
(1)
Core Networking
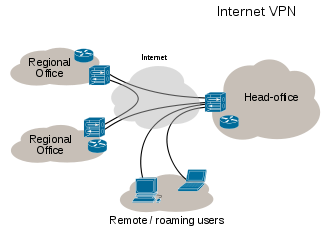
Connectionless packet switching and routing
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


0 comments:
Post a Comment